Causal Flows are statistically significant links between putative causal events (somatic mutations, copy number variations, chromosomal translocations, etc.) and the activity levels of regulators and regulons. In the causal flow, a mutation may causally activate or deactivate a downstream regulator which then might up- down-regulates a regulon that contains genes with similar expression profiles and binding sites.
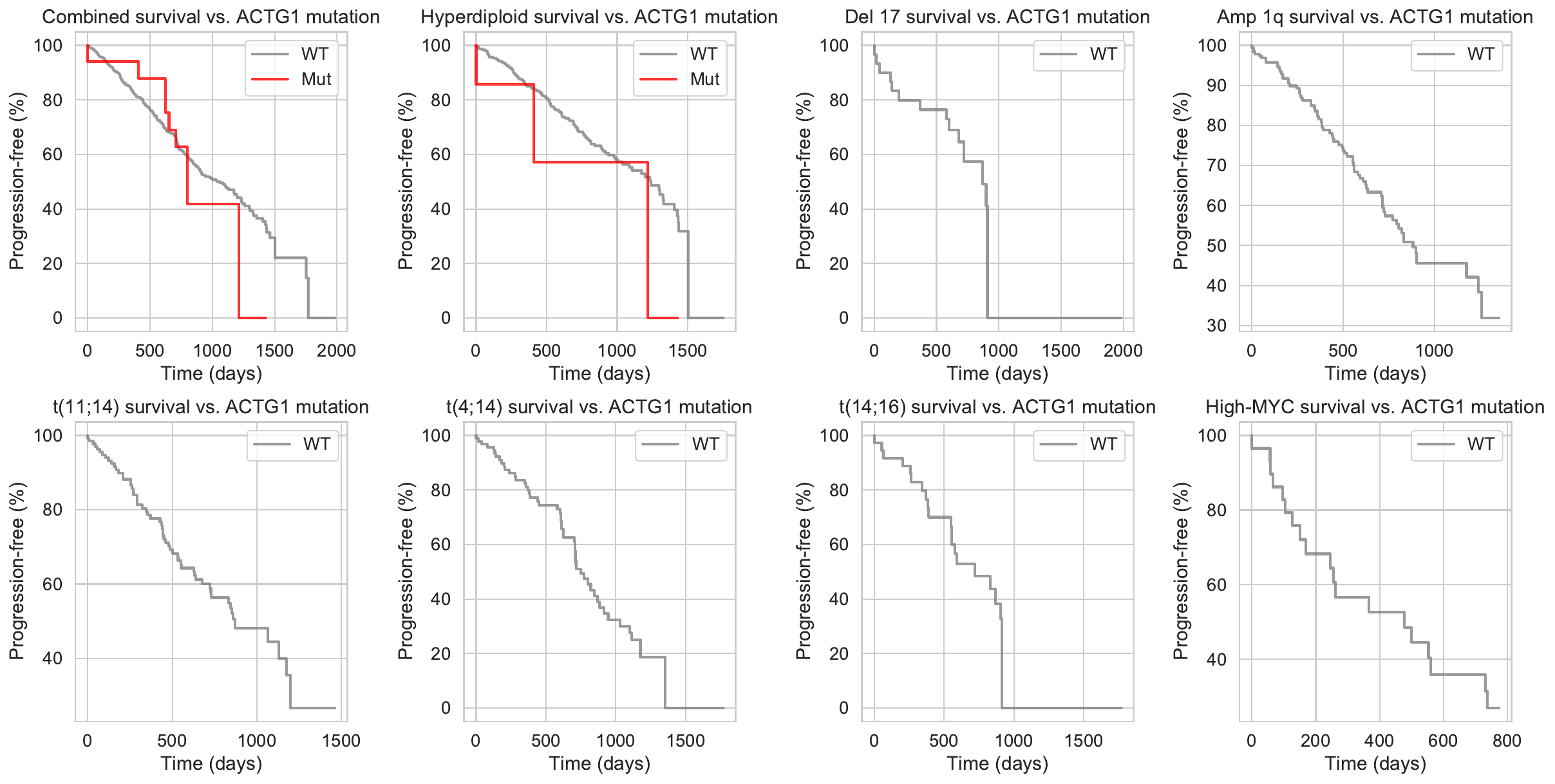
Causal Mechanistic Flows for Mutation ACTG1
| Regulator | Role | Regulon | Cox Hazard Ratio (Regulon) | Transcriptional Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETS1 | down-regulates | R-12 | -0.427939 | Pr-60 |
| ETS1 | down-regulates | R-13 | 1.07999 | Pr-93 |
| NR2F6 | up-regulates | R-1377 | -3.229 | Pr-137 Genes (22)KCNE3, SUGCT, SLC35A4, COX8A, PRR15, PFN4, FAM91A1, TMEM94, C14orf28, CMTR2, NQO1, FAM120C, PTPN1, SLC25A29, TMA16, MZT1, CSNK1E, KCTD7, CDK3, CHMP1B, COMMD3-BMI1 Regulons (23)R-2269, R-1302, R-186, R-1876, R-790, R-972, R-782, R-1579, R-1150, R-704, R-1950, R-1175, R-1457, R-1988, R-1345, R-713, R-3084, R-291, R-784, R-1348, R-2965, R-1533, R-1377 |
Mutation Causal Mechanistic Flow Network
Influences from mutations (magenta chevrons) to regulators (blue triangles) and then from regulators to the given regulon (red square) are indicated with colored edges. Red-colored edges denote up-regulation or activation while green colored edges represent down-regulation or repression.